II Freshmen PhD & Professional Cruise

II Freshmen PhD & Professional Cruise
Edition 2025
Event Overview
General Chair: Prof. Eng. Roberto Revetria, PhD
Program Chair: Dr. Eng. Anastasiia Rozhok, PhD
Event Dates: January 19th to January 24th
Departure Location: Marseille (France)
Destination: Rome (Civitavecchia) with stops in Barcelona, Palma de Mallorca and Palermo
Partecipants: 100+ researchers, professionals, and scholars from around the world
Program & Guest Lecture
Program
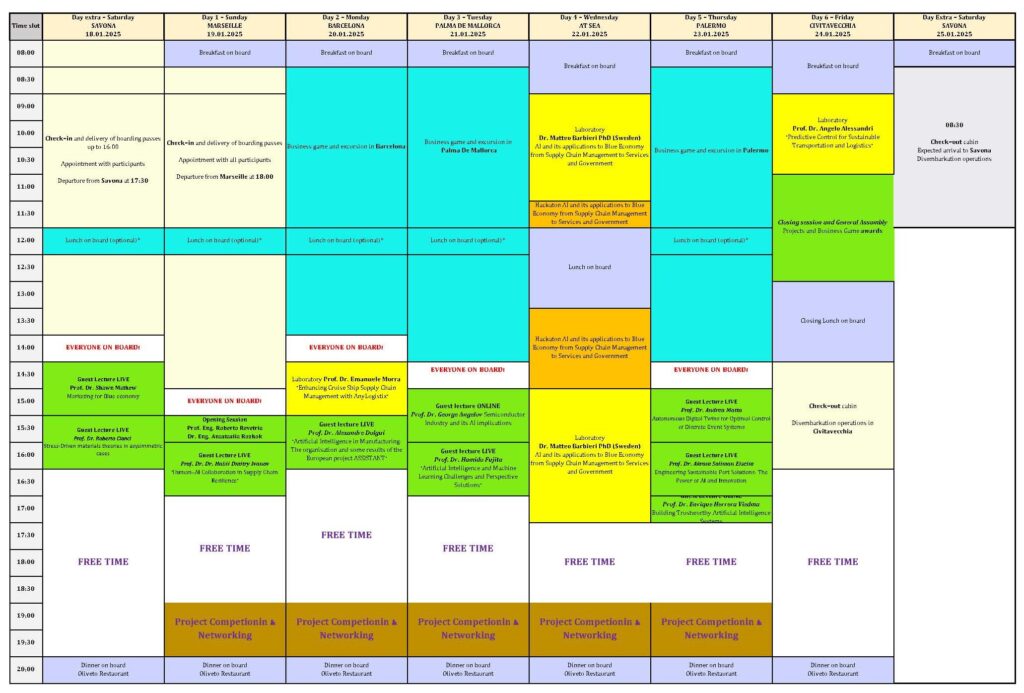
Guest Lectures
Laboratories
Professor Dr. Habil. Dmitry Ivanov’s lecture on “Human-AI Collaboration in Supply Chain Resilience“
In this talk, we discuss how human-based and AI-based decision-making support can be combined when managing supply chain resilience. Our talk focuses on an intelligent digital twin (iDT) framework. New digital technologies and artificial intelligence enable novel approaches and tools, allowing us to move from isolated models to intelligent decision-support systems. Our talk presents a comprehensive decision-making framework for leveraging digital twins in stress-testing and resilience analysis of supply chains. It outlines how digital twins can aid theoretical advancements in SC resilience and viability. An iDT is a system that combines human intelligence with AI to create a digital representation of physical supply chains, use cognitive AI capabilities, and create new knowledge about the system through mutual feedback between human and artificial intelligence. The iDT collects and processes data, employs analytics, mimics human decision-making, and develops new knowledge and decision-making algorithms through human-AI collaboration.
Prof. Dr. Dr. Habil. Dmitry Ivanov is a Professor of Supply Chain and Operations Management, director of the Digital-AI Supply Chain Lab, and faculty director of M.A. Global Supply Chain and Operations Management at the Berlin School of Economics and Law. His research spans supply chain resilience and digital supply chain twins. Author of the Viable Supply Chain Model and founder of the ripple effect research in supply chains. He gained Dr., Dr. Sc., and Dr. Habil. degrees and won several research excellence awards. His research record counts around 450 publications, with more than 160 papers in prestigious academic journals and the leading books “Global Supply Chain and Operations Management” (three editions), “Introduction to Supply Chain Resilience,” “Introduction to Supply Chain Analytics,” „Structural Dynamics and Resilience in Supply Chain Risk Management, ““Scheduling in Industry 4.0 and Cloud Manufacturing”, “Digital Supply Chain” and „Handbook of Ripple Effects in the Supply Chain“. He delivered invited plenary, keynote, panel, and guest talks at the conferences of INFORMS, IFPR, IFIP, IFAC, DSI, and POM, and over 30 universities worldwide. He has been Chairman, IPC Chair, and Advisory Board member for over 60 international conferences in supply chain and operations management, industrial engineering, control, and information sciences. Recipient of several prestigious academic awards. Principal investigator in several projects about digital supply chain twins and resilience funded by EU Horizon and DFG. Listed in several rankings as one of the most cited researchers in Business and Management. Chair of IFAC CC 5 “Cyber-Physical Manufacturing Systems,” Editor-in-Chief of International Journal of Integrated Supply Management, Editor of Annals of Operations Research, Associate Editor of International Journal of Production Research and OMEGA, guest editor and Editorial Board member in over 20 leading international journals including IISE Transactions and IJPE, to name a few.
Professor Dr. Alexandre Dolgui’s lecture on “Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing: The organisation and some results of the European project ASSISTANT“
In this lecture Prof. Alexandre Dolgui outlines the main idea and approach of the project. The project ASSISTANT (LeArning and robuSt deciSIon SupporT systems for agile mANufacTuring environments) is a large European project on Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Manufacturing with participation of 4 Industrial partners and 8 academic or semi-academic (research and innovation) organizations from different countries of EU. The project provided a set of AI-based digital twins system that helps process engineer and production planner to operate collaborative mixed-model assembly lines based on the data collected from IoT devices and external data sources. Such a tool helps decision makers in industry to design the assembly line, plan the production, operate the line, and improve process tuning. In addition, the system monitors the line in real-time, ensures that all required resources are available, and allow fast re-planning when necessary. ASSISTANT tool aims to make cost-effective decisions while ensuring product quality, safety and well-being of the workers, and managing the various sources of uncertainties. The resulting digital twin systems are data-driven, agile, autonomous, collaborative and explainable, safe but reactive. The ASSISTANT tools are based on the approach of extending generative design, an established methodology for product design, to a broader set of manufacturing decision making processes; and to make use of machine learning, optimization, and simulation techniques to produce executable models capable of ethical reasoning and data-driven decision making for manufacturing systems. Combining human control and accountable AI, the ASSISTANT toolsets span a wide range of manufacturing processes and time scales, including process planning, production planning, scheduling, and real-time control. They are designed to be adaptable and applicable in a both general and specific manufacturing environments. 3 case studies (from Siemens, Atlas Copco and Stellantis) were considered to test the tools developed. Examples of applications and some specific models and algorithms will be presented and discussed.
Professor Dr. Hamido Fujita‘s lecture on “Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Challenges and Perspective Solutions”
This lecture is dedicated to Ph.D students and young researchers to expose research challenges in terms of better quality in themes selection and investigation with innovation and creative thinking. I will outline my research experience and discuss journal scientific publications on hot topics in research and development in terms of quality. I have selected hot topics in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in supply chain and also operational research in terms of optimization and search techniques. The hot topics in training in Machine Learning is a crucial aspect that affects the system’s credibility in terms of performance and is employed for robust applications such as healthcare systems. Machines or algorithms, in wide challengeable applications in security or vision or health care early predictions, learn from data. Nevertheless, in most cases, the extensive and unbalanced data and noise make it unreliable in prediction accuracy. Supervised machine learning is and was one of the aspects of providing artificial intelligence-based solutions. However, this was limited due to the difficulty of labeling big data and many crucial problems in weak relations and noise in data. Semi-supervised learning, for example, Multiview learning, could assist in solving these problems. In many published research, there are still problems in providing machine learning models that are unbiased and efficient in terms of robustness and resilience in data-driven systems. Multiclass classification still has problems regarding clear definitions in class classification, bias, imbalance, and weak relations, making machine learning for multiclass classification insecure for classification or regression analytics. This causes limitations in applying such technology in medical applications and diagnosis prediction. In this lecture, I will outline these problems in our one-class classification project. These are related to providing more robust accuracy prediction with some uncertainty that can help us have more accurate classification and prediction. We have applied such findings in health care for heart sickness and seizure early prediction like in https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.107277 and https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102023 . We also have deep learning models, which have challenges related to evidential deep learning and fairness relative to data. There are essential issues in expanding research in evidential deep learning, in which uncertainty prediction of variational Auto encoders can provide decisions on evidential distribution, which in turn helps to provide a measure of uncertainty in decision. We currently have a research project titled “Healthcare Risk Prediction on Data Streams Employing Cross Ensemble Deep Learning,” supported by the Japan Science Promotion Society (JSPS). In this project, we have employed a one-class classification deep neural network for health care prediction. In this lecture, I will outline these perspectives and discuss challenging trends.
Professor Dr. Hamido FUJITA (Life Senior Member IEEE)
https://www.webofscience.com/wos/author/record/1136840 Executive Chairman of i-SOMET Incorporated Association, Japan https://i-somet.org/, Distinguished Professor: Iwate Prefectural University, Japan, Professor at Malaysia-Japan International Institute of Technology, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Editor-in-Chief: Applied Intelligence (Springer), Editor-in-Chief of International Journal of Healthcare Management (Taylor & Francis), Emeritus Editor-in-Chief: Knowledge-Based Systems, Vice President of International Society of Applied Intelligence, Doctor Honoris Causa (Óbuda University, Hungary), Doctor Honoris Causa (Timisoara Technical University, Romania). He is a Distinguished Professor at Iwate Prefectural University, Japan. He is also a contracted Professor at the Malaysia-Japan International Institute of Technology(MJIIT), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. He is also a Research Professor at the University of Granada (Spain), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, and HUTECH University Vietnam; Expert Excellence Professor at the Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences. He is currently the Executive Chairman of the i-SOMET Incorporated Association Japan. He is a Highly Cited Researcher in Cross-Field for the years 2019 and 2020, 2021, and 2022 in the Computer Science field, respectively, from Clarivate Analytics. He is Editor-in-Chief of Applied Intelligence (Springer), Editor-in-Chief of Healthcare Management (Tayler&Francis), Editor-in-Chief of Knowledge-Based Systems (2010-2020), and Emeritus Editor of Knowledge-Based Systems
https://www.webofscience.com/wos/author/record/D-6249-2012
Professor Dr. Andrea Matta’s lecture on “Autonomous Digital Twins for Optimal Control of Discrete Event Systems“
With the coming of the Industry 4.0 wave, digital representations of production systems have been promoted from marginal to central. Digital twins are not simply conceived as simulation models of their physical counterparts for offline what-if analysis, differently they are developed as self-adaptable and empowered decision-makers timely aligned with the dynamics of the real system. Enriched by these new features, digital twins are widely recognized as the key enablers for the implementation of optimal control of smart manufacturing systems. Despite this new role, there are significant barriers to the adoption of the digital twin concept in industrial applications. The creation and update of digital twin models is still a challenge because of the high skills required to use the simulation applications available in the market, the long development times, and their difficult integration with optimization and artificial intelligence packages. The frequent changes manufacturing systems encounter in their life cycle boost these issues making the system model and the control most rapidly obsolete. This talk describes data-driven approaches for generating and controlling multi-fidelity models for digital twins of manufacturing systems from data acquired from sensors also in non stationary situations. Application examples will also be presented.
Professor Dr. Andrea Matta is Full Professor of Manufacturing and Production Systems at Department of Mechanical Engineering of Politecnico di Milano. He graduated in Industrial Engineering at Politecnico di Milano where he develops his teaching and research activities since 1998. He was Distinguished Professor at the School of Mechanical Engineering of Shanghai Jiao Tong University from 2014 to 2016 and Guest Professor between 2017-2019. He has been visiting scholar at Ecole Centrale Paris (France), University of California at Berkeley (USA), and Tongji University (China). He is member of the technical committee of MADE Competence Center. His research area includes analysis, design and management of manufacturing and health care systems. He has published 190 scientific papers on international and national journals/conference proceedings. He is Editor in Chief of Flexible Services and Manufacturing Journal since 2017, past member of editorial board of OR Spectrum journal and IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters journal. He is member of scientific committee in several international conferences. Member of the Steering Committee of PhD on Mechanical Engineering. Member of the ADA University Advisory Board. He was awarded with the Shanghai One Thousand Talent and Eastern Scholar in 2013.
Prof. Dr. Akram Soliman Elselmy’s lecture on “Engineering Sustainable Port Solutions: The Power of AI and Innovation“
Engineering is a vital factor that drives sustainable port development. This development aims to reduce maritime activities’ environmental impact and ensure coastal ecosystems’ long-term viability within the blue economy general frame. By consolidating the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and innovative engineering solutions while adapting to the World Port Sustainability Program (WPSP) Principals, ports can optimize operations, reduce emissions, and enhance sustainability. In this state-of-the-art lecture, Prof. Akram Elselmy will explore some of the key applications of AI in port management, including traffic optimization, energy efficiency, and environmental monitoring. Furthermore, innovative engineering case studies will be presented at the end of the lecture to provide a better perspective of the topic. By understanding the role of AI and engineering in creating sustainable port solutions, young Engineers, especially those interested in such a topic, will gain valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities within this growing field. This knowledge will equip them with skills and expertise that will help them work on innovative solutions that address the pressing environmental and economic issues facing ports. As the world increasingly focuses on sustainability, there is a growing demand for engineers who can design and implement sustainable port infrastructure and operations.
Professor Dr. Akram Soliman Elselmy, is a Professor of Port Planning and Coastal Engineering, and the dean of College of Engineering and Technology at the Arab Academy for Science, Technology & Maritime Transport. He was the Dean of Port Training Institute, AASTMT from 2008 to 2022. He is a Consultant Engineer of Harbours Planning, Navigation and Shore Protection. He got his PhD 2004 from the School of Civil Engineering, University of Nottingham, UK. Prof. Akram has more than thirty-two years of experience in Port Planning and Coastal Engineering. He also has many distinguished research activities, as he supervised many PhD and MSc theses, in addition to publishing more than fifty research
papers in many international journals and conferences in the fields of Port Planning, Coastal Engineering, Coastal Zone Management and Sustainable Development. He has been the head of the International Maritime Transport and Logistics Conference Organizing Committee, MARLOG, since 2011. Prof. Akram is the Editor in Chief of the International Maritime Transport and Logistics Conference Proceedings, SCOPUS indexed proceedings. He is a Member of the Scientific Program Committee of the 16th International Conference on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation TransNav 2025, Member of the PIANC WG for Guidelines for Inland Waterways Infrastructure to Facilitate Tourism, Member of the Peer Reviewer Committee of the Journal of Marine Policy (JMP) and a member of the Peer Reviewer Committee of the International Associations of Maritime Universities Conferences (IAMU). Prof. Akram is the project Manager of the” YOUTH EMPLOYMENT IN PORTS OF THE MEDITERRANEAN ENI Funded Project by CBC (Cross Border Cooperation) Program (September 2020 to December 2023) (https://www.enicbcmed.eu/projects/yep-med). Furthermore, he acts as a Consultant for the project titled “Studying the Vulnerability Assessment of Egyptian Ports to Climate Change and Appropriate Adaptation Options Based on Cost-Benefit Analysis” – Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) Funded Project (for the Ministry of Scientific Research).
Professor Dr. George Angelov’s lecture on Semiconductor Industry and its AI implications
George Angelov is Deputy Minister of Innovation and Growth and Professor in Microelectronics at the Technical University of Sofia. He received MSc degree in Physics from Sofia University “St. Kliment Ohridski”, Bulgaria in 1999 and PhD degree in Microelectronics from Technical University of Sofia, Bulgaria in 2008. From 1999 to 2002 he was with Technology Centre–Institute of Microelectronics, Sofia, Bulgaria. From 2007 to 2012 he was Assistant Professor, from 2013 to 2021 he was Associate Professor and since 2022 he has been Professor at the Department of Microelectronics, Faculty of Electronics Engineering and Technologies (FETT), Technical University of Sofia. George Angelov was Chair of Department of Microelectronics (2015-2023), Chairman of the Managing Board of the Cluster of Microelectronics and Industrial Electronics Systems (2016-2023), Head of MINOLab at Sofia Tech Park (2017-2023) and Director of Information and Public Relations at the Technical University of Sofia (2020-2023). George Angelov’s business interests are in entrepreneurship, business development, technology transfer, and innovations management. His research interests are in semiconductor device modeling (FinFETs, nanosheet FETs, nanowires, junctionless transistors, CNTs, etc.), design of integrated circuits, failure analysis (FA), microelectronics reliability (EMC & ESD), bioelectronics, energy storage and battery management systems, energy efficiency – monitoring and control systems. George Angelov is author of 125 papers, 4 books, and 1 monograph. Member of IEEE (since 2003) – Solid-State Circuits Society and Electron Devices Society; Marquis Who’s Who in the World (since 2008).
Professor Dr. Shawn Mathew’s lecture on “AI-Driven Public Policy: Harnessing Emerging Technologies for Governance and Social Good“
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and emerging technologies are driving significant advancements in public policy and governance, offering innovative solutions to address complex societal challenges. These technologies enable data-driven decision-making, creating opportunities to enhance efficiency, transparency, and inclusivity in governance systems. This talk examines how AI applications such as predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, and decision support systems are reshaping policy frameworks and public administration on a global scale. Examples include AI-powered urban management systems that optimize resource allocation and reduce traffic congestion, as well as public health platforms that utilize real-time data to combat pandemics effectively. The discussion highlights AI’s applications in areas such as disaster response, fraud detection, and citizen engagement, showcasing its potential to improve societal outcomes. Addressing challenges like algorithmic bias, privacy concerns, and infrastructure limitations is essential to ensure responsible implementation. Regulatory frameworks, such as the European Union’s AI Act, provide guidance for balancing technological innovation with ethical considerations. Emerging research opportunities in this field include the development of scalable AI systems for resource allocation, the creation of ethical frameworks for AI governance, and innovative methodologies for integrating emerging technologies into public systems. By aligning technological advancements with ethical principles, AI has the potential to serve as a catalyst for sustainable development, equitable governance, and societal progress. The vision presented emphasizes the transformative potential of AI and emerging technologies to build inclusive and adaptive systems that address the evolving needs of society in the 21st century.
Professor Dr. Shawn Mathew holds the position of Senior Lecturer in Marketing at Middlesex University Dubai. He completed his Doctorate in Marketing from the Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad (IIMA) and holds a B.Tech. degree in Computer Science and Engineering from Mahatma Gandhi University, India. With a wealth of academic and corporate experience, Dr. Mathew’s journey has been marked by significant contributions. Before his association with Middlesex University Dubai, he held various academic responsibilities, including serving as the Chairperson of the PGDM Dual Country Program (DCP), Chairperson of the Marketing Area, and Assistant Professor of Marketing at IMT Dubai. He also served as Faculty of Marketing and Co-Chairperson of Admissions at both IMT Ghaziabad and the Indian Institute of Management Jammu. Dr. Mathew’s academic engagements also included visiting faculty positions at renowned institutions such as IIM Kozhikode, IIM Amritsar, IIM Ranchi, and IIM Shillong. Prior to transitioning to academia, he gained valuable corporate experience through roles with prominent multinational companies like Cognizant Technology Solutions (CTS) and the A.P. Moller – Maersk Group. Dr. Mathew is a registered member of The Global Association of Applied Behavioural Scientists (GAABS) and a member of the Society for Judgment and Decision Making (SJDM). His accomplishments also include being an American Marketing Association (AMA) – Sheth Foundation Doctoral Consortium Fellow (2011) and an AIM – AMA Sheth Foundation Doctoral Consortium Fellow (2014). He participated as an invited participant at notable academic events, including the Max Planck Summer Institute on Bounded Rationality (2017) and the TAPMI-Max Planck Winter School on Bounded Rationality (2017). Dr. Mathew’s academic recognition extends to being a semi-finalist for the Pareto Fellowship (Centre for Effective Altruism, Oxford University, 2016), as well as being selected as one of the winners of the Liam Glynn Travel Scholarship (2011).
Professor Dr. Roberto Cianci’s lecture on “Stress-Driven materials theories in axysimmetric cases“
In this laboratory we study a circular plate of non-local gradient material with specific characteristics. A stress-driven approach is used. Differential equations are obtained and, for plates of large radius, they are solved analytically. It is highlighted that the displacement on the lateral surface is a function of the non-local parameter, unlike the resulting moments. A finite element solution using the Galerkin method is presented when considering a solid circular plate. The boundary conditions are studied on the outer radius.
Professor Dr. Roberto Cianci is a distinguished Professor of Mathematical Physics at the University of Genoa, where he has been shaping the academic and research landscape with his expertise in mathematical modeling and simulation. With a career spanning decades, Professor Cianci has made significant contributions to his field, particularly in the study of continuous simulation and the applications of mathematical physics to complex systems. Since 2017, Professor Cianci has served as a member of the editorial board of SNE Simulation Notes Europe (ISSN: 2306-0271), a prestigious journal dedicated to advancing simulation methodologies and their real-world applications. His editorial work reflects his commitment to fostering innovative research and maintaining rigorous academic standards in simulation studies. Professor Cianci’s academic journey is marked by active involvement in international research initiatives. Since 2011, he has been a key contributor to the Mathematical Physics research program of SIGRAV (the Italian Society of General Relativity and Gravitational Physics), where he collaborates with leading experts to explore the interplay between mathematical models and gravitational phenomena. In addition to his academic appointments, Professor Cianci has held the role of Scientific Coordinator for the “Continuous Simulation Modelling” program under the Liophant Society since 2013. In this capacity, he has spearheaded initiatives aimed at advancing the understanding and application of continuous simulation in diverse scientific and industrial domains. Professor Cianci’s work is a testament to his passion for blending theoretical rigor with practical applications. His research bridges disciplines, pushing the boundaries of how mathematical principles can solve real-world problems. Through his teaching, editorial contributions, and leadership in international collaborations, he continues to inspire the next generation of scientists and researchers.
Dr. Matteo Barbieri (PhD, Sweden)’s laboratory on “AI and its applications to Blue Economy from Supply Chain Management to Service and Government”
Dr. Matteo Barbieri’s lectures and labs will be focused on the current state of AI in industry, with practical examples of implementations of services based on AI models. Lectures will include success and spectacular failures stories from his experience, suggestions for those who want to embark in a similar journey and an acceptable amount of meme-based slides. No specific knowledge in ML is strictly required, just bring your laptop, VS code and your curiosity.
Dr. Matteo Barbieri got a PhD in Computer Science from the University of Genoa in 2017, working in the field of Machine Learning applied to the analysis of biomedical data. His interest has since shifted to the productionalization of AI-based solutions in various industries. Matteo moved to Sweden in 2020, and is now a Senior Machine Learning Engineer at Epidemic Sound.
Professor Dr. Angelo Alessandri’s laboratory on “Predictive Control for Sustainable Transportation and Logistics”
The considerable growth of transportation has made the development of decision support systems to deal with problems of sustainable transports a topic of crucial importance. The efficient management of urban/freeway traffic, container terminals, and logistics networks may become the subject of a course where the most important methodologies available from Operations Research and Control Theory are presented to deal with problems concerning the efficient exploitation of limited resources. Typical examples of such management problems will be considered in an increasingly involving teaching path with lessons of both theory and practice. The first type of lessons is devoted to the basic principles of Automatic Control and Optimization. In the second ones, case studies concerning logistics operations at container terminals and distribution in supply chains will be illustrated. In the course various subjects will be addressed, as it is briefly described in the following. The first subject regards the modelling of complex systems to simulate and analyze their behaviour over time. This is important, for example, when one wants to evaluate the performances of a container terminal. Standard results from queueing theory were employed in the past with the main drawback of suffering from a poor capability of describing the dynamic behaviour of a terminal. As a consequence, to take into account also dynamic aspects, more powerful modelling paradigms were proposed like, for example, discrete-event systems. Discrete-event tools allow one to construct very precise models, but, unfortunately, they are quite demanding from the computational point of view. Such difficulty arises particularly when a model is used to devise management strategies for a container terminal or a distribution chain in real-time due to the large number of variables, even if one has to deal with small container terminals or distribution networks of small companies. Generally speaking, the availability of a model with a convenient trade-off between precision and computational burden make possible to formulate control problems that aim at exploiting the available resources as much efficiently as possible. For instance, the productivity of a terminal depends on the efficient exploitation of labour and equipment. An increased efficiency can be obtained by a more convenient use of the available transfer machines. Toward this end, a predictive control approach appears particularly appropriate, as it is based on the idea of solving an open-loop finite-horizon optimal control problem at each time step and applying only the first control action. Optimization is performed over a forward horizon from the current time instant by using the available information about the container occupancies in the various areas of the terminal, and the foreseen import and export flows of the various carrier classes. Predictive control is the second main subject of the course. One of the main advantages of predictive control concerns the ability to consider constraints on both state and input variables of the model. These constraints are very important in the two considered case studies. For example, the space limitations in the yard can be easily taken into account via upper bounds on the state variables that represent the number of containers in the various areas of the terminal. The maximum inventory levels can be treated similarly in the management of a distribution chain, as well as the limitation concerning the capacity of the carriers of the various types of goods. Further constraints can be introduced to account for the available resources that are needed to perform the transfer operations. Moreover, the reduced availability of berths, parking lanes, and rail platforms requires the introduction of binary variables that represent the beginning, progress, and conclusion of such operations. In the case of distribution chain problem, integer variables are needed to account for the periodic replenishment of goods at fixed intervals of buckets. The solution of the predictive control problem becomes more difficult to find when binary or integer variables are introduced. The use of nonlinear dynamic model nonlinear cost functions makes the resulting optimization problem to solve of mixed-integer nonlinear programming type, for which different methodologies can be used, like branch-and-bound and cutting-plane. Such topics will be addressed as third main subject of the course, i.e., the application of optimization. The proposed course is inspired by the success obtained by predictive control in the control of chemical process and manufacturing. This success indicates that one can expect the rapid diffusion of such paradigm to the management of complex systems, where significant advantages in terms of sustainability can be gained via an increased efficiency in the exploitation of the resources such as power systems and supply chains.
Professor Dr. Angelo Alessandri received the “Laurea” degree in Electronics Engineering and the Ph.D. degree in Electronics and Computer Engineering from the University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy, in 1992 and 1996, respectively. From 1996 to 2005, he was a research scientist with the National Research Council of Italy, Genoa. In 2005, he joined the University of Genoa, where he is currently a full professor in the Department of Mechanical, Energetics, Management, and Transportation Engineering. His main research interests include estimation, fault diagnosis, and optimal control. He was an associate editor of the IFAC Journal of Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, the IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, and the IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology. He serves as an editor of the International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing and as an associate editor of the EUCA European Journal of Control and of the IFAC journal Automatica.
Professor Dr. Emanuele Morra’s laboratory on “Enhancing Cruise Ship Supply Chain Management with AnyLogistix“
As part of this workshop, I will guide participants through the use of AnyLogistix, a powerful tool for supply chain modeling, optimization, and simulation. We will explore how the unique operational challenges of cruise ships, including onboard logistics and port-to-port supply management, can be optimized to increase efficiency. Through live demonstrations and case studies, participants will learn to develop models, run optimization algorithms, and simulate what-if scenarios. The goal is to equip attendees with practical skills in leveraging advanced software to address the complexities of the cruise ship supply chain and improve overall performance. Additionally, the workshop will feature an interactive digital lab where participants will be divided into teams, each tasked with planning a virtual itinerary for a luxury cruise ship. Teams will face unique challenges posed by extreme destinations such as Antarctica, the Arctic, or the Galapagos Islands, where ensuring adequate supplies and resources becomes critical. The exercise will simulate real-life supply chain scenarios, including the management of fuel, food, and medical supplies, while navigating difficult environmental and logistical conditions. Each team will also need to propose solutions for managing an emergency situation onboard, such as a mechanical failure or medical emergency, requiring immediate resource allocation and decision-making under pressure. This hands-on approach will allow participants to apply their knowledge in real-time, using AnyLogistix to test and refine their strategies for maintaining an efficient and resilient cruise ship supply chain.
Professor Dr. Emanuele Morra is External Professor at the Politecnico of Turin (ITA) in Industrial Plants and Safety. He is Partner of MEVB Consulting Gmbh, a consulting Company with international expertise in simulation and modelling with base in Olten (Switzerland). He is trainer and developer for simulation models in Supply Chain and Industrial Plants, based on anyLogistix and Anylogic softwares. He is reviewer for scientific paper for ASTESJ Journal, Home – Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal (astesj.com).
Resources








Publication Opportunity/Proceeding
As part of the II Freshmen PhD & Professionals Cruise School 2025, participants will have the exciting opportunity to present their research projects during the conference. Selected projects will be considered for publication in a Scopus-indexed journal, providing a valuable platform to share your work with the international academic community.
To be considered for publication, participants must submit an abstract of their project via the official submission form. Projects that align with the conference’s focus on AI and sustainability in industry, healthcare, and government will be given priority.
Publication Details:
• Selected papers will be published in the journal Special Issue, “Transition to Industry 4.0 in Emerging Domains: Methodology and Case Studies.”, which is indexed in Scopus.
• The journal welcomes both theoretical and applied research related to AI applications in supply chain management, healthcare, transportation, and sustainable development.














 Users Today : 38
Users Today : 38 Total Users : 13489
Total Users : 13489 Views Today : 77
Views Today : 77 Total views : 29739
Total views : 29739 Who's Online : 1
Who's Online : 1